These past few weeks I’ve been thinking a lot about portraits in painting and the art of portraiture. This is perhaps hardly surprising as I needed to think about a cover for my new Roman story and also started a hashtag project on Twitter and Facebook (#FreePortraitFriday), where authors can share a description of their main characters and I’m going to pick one to do a free character portrait.
Those are excellent exercises for me as I don’t just have to think about how to visualize the verbal physical descriptions of a character, but also how to visualize the…eh…character of said character. Like, is that person shy or self-confident? Kind? Arrogant? Mischievous? Those character traits will translate into the pose and expression and are nearly as important as the physical characteristics.
A couple of years ago, there was an exhibition of children’s portraits at the Städel, a famous art museum in Frankfurt, and while I didn’t manage to go and see it, I did manage to snatch up a catalogue of the exhibition. The catalogue doesn’t just provide the reader with a good overview of the history and development of children’s portraits, but also invites the reader to look more closely at the small details. When you look at Joshua Reynold’s portrait of little Frances Crewe from 1775 (“Miss Crewe“), when more realistic portraits of children that emphasized their individual personalities rather than family and heritage, had just become all the rage, you can easily see what a sweet, funny little girl Frances must have been.
For his portrait of young Lewis Cage, the artist Francis Cotes chose a pose reminiscent of that of military heroes, hinting at the boy’s self-confidence. However, he immediately subverts this pose and we are reminded that this is a little boy, for in contrast to the men depicted in those military portraits, young Lewis looks far from neat and tidy: his waistcoat is unbuttoned, a corner of his shirt is hanging out of his breeches, which have become unbuttoned at his left knee. All those details add to the vitality of the portrait by hinting at the vitality and physicality of the child: he is dirty, sweaty, and stinky, but immensely proud of his achievements in cricketing.
And all those paintings of little children cuddling with their pets with obvious affection? How cute are those? Joshua Reynolds’ little “Miss Jane Bowles” (1775) exuberantly hugs her (long-suffering?) pet spaniel while smiling mischievously. And when Henry Raeburn painted his step-grandson in 1814 (“Boy and Rabbit“), he depicted little Henry as an affectionate young boy who tenderly cradles his white pet rabbit in his arm.
Posing is something I find rather difficult when I’m working with my digital models (and not the least because digital models don’t automatically pose naturally and, thus, if you don’t do it correctly you end up with a wooden-looking zombie — NOT the kind of look you really want to go for) (unless you’re doing a picture of a zombie, of course). To find the right pose (and the right camera angle) for a character often takes me quite a long time, and I typically need several test runs before I come up with something I’m happy with. As with those real-life portraits, it’s often the small details that add character to cover art.
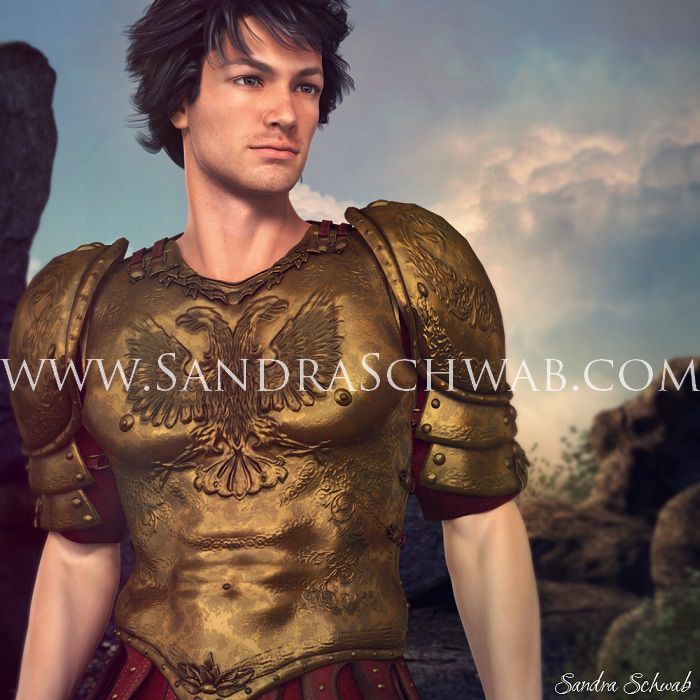
A few days ago I got thinking about what to do with the cover of THE CENTURION’S CHOICE. Which of my two guys should I put on the cover? Lucius, whom I used on the teaser image? Or Caius, the centurion from the title of the novella? In the end I settled on burly, cranky Caius – and after some puttering around, I ended up with the above picture. (I wasn’t able to find a digital version of a centurion’s armor, so I put Caius in a set of shiny Spartan armor.) But somehow, it just wasn’t quite right. I mean, he’s a good-looking dude, yes, but he looks a bit young-ish, and besides, Caius is described as being built like an ox. And this guy isn’t quite what I would call burly. So…more tinkering ensued!
Luckily, the muscles of digital models can be pumped up on demand and so I did some pumping (gosh, that was too much….), tried to add some muscle definition to his lower arms, and…oh, what about body hair? *Sandy wanders off to investigate digital options of adding body hair, comes back slightly traumatized* Um. No body hair, sorry.
But I did change the camera angle somewhat and turned his hair windswept to make the whole thing look a bit more heroic. And finally, I ended up with – taaaahdaaaaah! – this cover draft. Which I quite like. 🙂 And I hope you do too!
 THE CENTURION’S CHOICE will come out in late November / early December and will be my very first m/m story.
THE CENTURION’S CHOICE will come out in late November / early December and will be my very first m/m story.